How to be creative and favor innovation? In order to answer this question, we’ve organized a webinar with Luc de Brabandere, Fellow of the Boston Consulting Group and creativity expert, on:
- What is creativity?
- How to be creative while embracing constraints?
- What are the methods to be creative?
Luc de Brabandere has already co-edited several courses on Coorpacademy, such as Organizing and Facilitating a Creativity Session and Cognitive biases: thinking traps. He’s a Fellow at the Boston Consulting Group and the founder of Cartoonbase, an agency where consultants and artists work together.
If you want to discover the webinar replay, it’s here (in French).
As you probably guessed it, we’re going to speak about creativity in this article. Let’s start with a question in order to warm up.
Creative thinking relies mostly on our capacity to:
- Invent?
- Change our views, the ways we look at something?
- Follow our intuitions?
For Luc, creative thinking relies on how we change the ways we look at things. And he has 3 little stories, from the history of transportation through time, to illustrate.
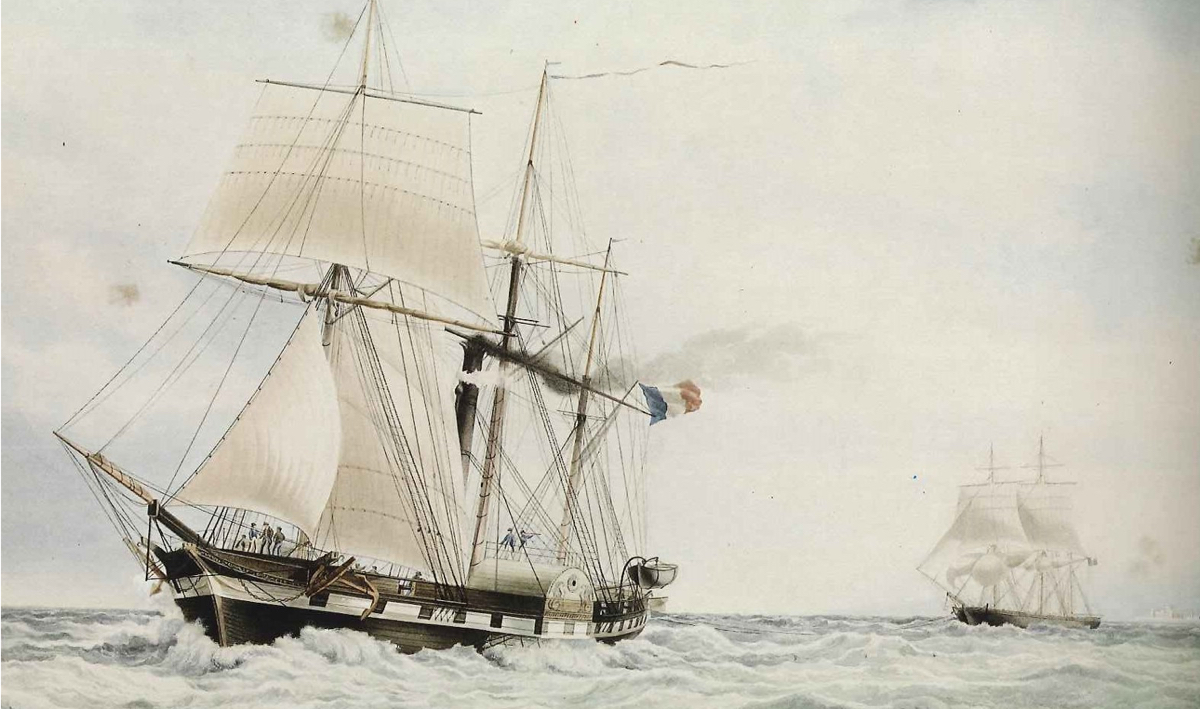

This is a boat that existed 200 years ago and that belonged to the French Navy, called the Sphinx. This boat is quite particular: it’s hybrid. We can see sails, but also something that looks like a steam engine. It’s then interesting to ask ourselves: How did people see this boat?
Let’s imagine two people, on the beach, looking at the Sphinx. Let’s imagine one of them is a bit conservatory, he doesn’t like change or new innovations. This person might describe the boat as: “I’ve seen a sailboat on which someone added a steam engine – why not? Maybe it will be efficient when there won’t be any wind.”
But now let’s imagine someone more creative, who is constantly changing the way he sees things. Someone more creative would say: “I’ve seen a steamer! Although we’ve kept the sails – maybe they can be useful if the engine is broken – but I’ve seen a steam boat!”
There’s a big difference!
Someone not changing his views will see steam as an addition to something that already exists, whereas someone changing his view will see a brave new world, the world of steam Navy!

This next picture is the consequence of not changing the ways we look at things. This is the biggest sailboat ever built, 50ish years after the Sphinx… So big nobody really knew how to maneuver it!
We can see that if nobody changes views, we end up in the field of “more the same thing”, maybe bigger, nicer, stronger, but still the same thing.
The real message conveyed by creativity is “something else”!

Let’s take the example of the velocipede. We have to understand that nobody really invented the bike as we know it today! The velocipede, velos, fast, pede, foot. The first engine was actually an engine to make your feet go faster – as in the image. What happened next? Someone using a velocipede, in a descent, realized he didn’t need his feet anymore, that the velocipede was moving by itself. And he wanted to climb up the hill after the descent, without using his feet again, so he thought about putting pedals on the velocipede. To make it a bike.
With this story, we see that ideas and innovation are only one half of the process. Creativity is the capacity to question at least one the hypothesis subtending the way we see the world. Innovation is the capacity to act once we’ve question the hypothesis. Let’s take a third example.

Still in the world of transportation: let’s take a look at the wagon. Not the whole locomotive, but the sole wagon. We can see how it’s built: like a sum of three diligences. 
The central part of the diligence is a U with two doors. We can see that the wagon is built like a sum of those same Us. From that observation, we see two ways of doing. You can be in the more of the same thing and yes – the wagon is better than the diligence, but it’s still more of the same thing. Or you can be in the other thing. That’s how Luc will define creativity and innovation: Innovation is the ability of an enterprise to change things, creativity is the ability for individuals to change their views, to change the way they look at the world: it is not the same thing!
One of the great creative people of History is Nicolas Copernic. His finding, the heliocentrism versus geocentrism, was a huge finding but had no impact on the solar system – at all! The solar system is still the same today as it was before Copernic. Copernic represents pure creativity. For enterprises, the issue is that they have to be better than Copernic. They have to be creative, to change the way they look at this, but they also need to act and to innovate after.
Now that we have defined creativity, let’s study creativity under constraint. And let’s start with an other question.
What do these three art pieces have in common?
- A Void by Georges Perec
- Amélie by Jean-Pierre Jeunet
- Boléro by Maurice Ravel
What do Maurice Ravel’s Boléro, Jean-Pierre Jeunet’s Amélie and Georges Perec’s A Void novel have in common? These works of art are all about embracing constraints. The lipogrammatic novel A Void was written entirely without the letter ‘e’, the movie Amélie was produced on a tiny budget and Maurice Ravel’s Boléro was almost entirely composed in C major.
We now want to prove that the friendship, the partnership and the complicity between constraint and creativity exist! Even though these three examples come from the world of arts, there is the same thing in science: people are creative because (thanks to?) of constraint, restrictions. Let’s illustrate this with an other story.

This is the story of Galileo. Galileo was convinced that Aristotle was wrong. Aristotle was saying that a falling body was falling at a constant speed. And it goes so fast that it’s hard – impossible – to measure it on the naked eye. There was also no timer, no video, no laser, nothing during Galileo’s times. But he was convinced that a falling body didn’t have a constant speed. And he had an extraordinary idea of creativity. As he was not able to measure it with his eyes – because the body is falling way too fast – he thought about measuring it and prove it with his ears. He then built the inclined plane you can see on the image below.

You can find this inclined plane at the Galileo Museum in Florence, Italy. Galileo started playing with bells, positioned them all along the plane and left a ball fall along it. He realized that if he was putting the bells following a geometric trajectory (1 – 2 – 4 – 8), that the bells would ring on a constant rhythm. So that there was an acceleration in the fall. He also was able to calculate the acceleration. Ideas like that one are born in the constraint!
In companies, it’s the same thing. What we are living with lockdowns has been a tremendous source of creativity. We all had to invent because of these restrictions. Numerous ideas wouldn’t have been born if it wasn’t for the constraint, the restrictions.
As a philosophy teacher, Luc had to question his students. Every year, he was doing it differently, in a classroom. This year, it was not possible. He had to come up with new types of questions. Such as: “Imagine you are a CEO and you hire in your company Aristotle, Plato, Kant and Descartes. Where would you put them?” This new type of question, invented because of the constraint, worked very well amongst students. And as students were placing Aristotle in Research & Development, Descartes in controlling and Kant in Human Resources, the engagement showed that from restrictive times comes new creative ideas.
Constraint is creativity’s friend.
We can also create the constraint within companies in order to favor creativity. It’s always a good idea to start with words. For example, asking people to describe their jobs without using the five words they usually use to describe them. You will then see people changing their views on their jobs. If you ask a train company to describe its job without using the words “trains” or “stations”, they will have to speak differently about their job! It’s one advice, but there are plenty of ways of stimulating creativity!
Restrictions push us further. In poetry, Alexandrian are for example a great constraint, pushing authors far beyond their limitations and their creativity!
Now that we’ve seen the relationship between constraint and creativity, let’s tackle the creativity session process and how to make it successful!
To succeed in organizing a creativity session, it’s like:
- Whipping up a mayonnaise: you would need the good ingredients, a good recipe and a clear method?
- Finalizing a puzzle: you would need to know or imagine the result in advance, have the big picture and a bit of feeling and luck?
- Having a satellite in orbite: you would need the final idea to continue its course and development when the session in over?
For Luc, organizing a good creativity session is like having a satellite in orbite. A new idea produced by a creativity session is like a little gem, put in orbite by a rocket called “creativity methods”, “creativity sessions” or “brainstorming.” The method itself takes a lot of time and energy, but the most important is what comes out of it, the idea, the gem, which will continue to live once the session is over.
Imagine someone in front of a piano, with his hands tied up. You would think that this person doesn’t know how to play piano. Untie the hands, the person still doesn’t know how to play piano, because he never learned. There are two elements in creativity. The first one is to loosen the bonds, untangle the ropes, to free people by changing their views. But once you are free, you can apply methods. In the piano example, it’s the music theory. Creativity methods exist and are extremely useful.
Luc thinks that creativity also has rules, and that you can play better than others if you understand the rules. Let’s take an other example.

This is the Apple 1. A lot of people think that the first personal computer was the Apple 2, but it wasn’t! The first is the one displayed in the picture, that you can see in the Apple Museum in Praha, with an instruction manual signed by Steve Wozniak himself! What you have in this picture is the first creation of a company that is now worth more than the whole CAC 40! But at the times, if you would ask someone: “Is this a good idea?“, there would be thousands of reasons to say no! This looks too big, this will fall into pieces, we are going to get burnt by the engine, etc.
 Let’s take a look at this cartoon. It is essential. We have to remember that the human brain has two speeds. Two completely different speeds and ways of working.
Let’s take a look at this cartoon. It is essential. We have to remember that the human brain has two speeds. Two completely different speeds and ways of working.
The first one is imagination, opening, divergence. The second one is convergence, choice, decision. Those two brains don’t work together and keep fighting each other. We need to respect them. And always think that a new idea is never good. And it’s never bad!
In a creativity session, when someones comes up with an idea, the important thing is not to judge it! Never say : “Yes, but…” Of course, a new idea is never good. But this is the most important moment of the session. If you say: “Yes, but…“; you kill the idea, you forget it, you go on onto something else. If you say: “Yes, and…“, well, sometimes, you win the jackpot!
One last piece of advice to be creative: changing habits! Don’t go in the same restaurant than usual, don’t take the same route to go to work, buy a newspaper you are not interesting it. Disrupt your ways of doing things. Maybe great ideas will come out of it!













 Let’s take a look at this cartoon. It is essential. We have to remember that the human brain has two speeds. Two completely different speeds and ways of working.
Let’s take a look at this cartoon. It is essential. We have to remember that the human brain has two speeds. Two completely different speeds and ways of working.